
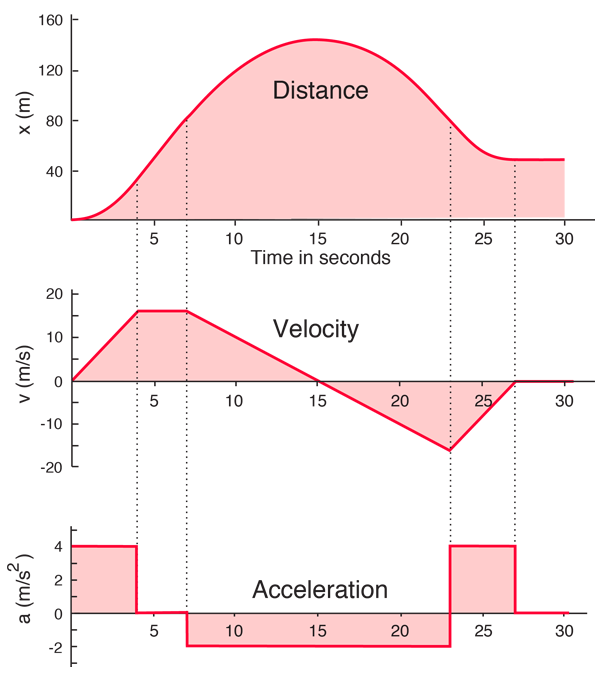
The speed of travel (of any particular section of the graph) can be calculated via the gradient.Ī gradient is calculated by using this formula:
This means that the velocity will also be 0 as a result (since 0/2000 = 0).ĭistance-time graphs – Plots distance traveled versus time. Therefore, in that sense, you haven’t actually moved from your original starting point A, and therefore your displacement is actually zero. In other words, your starting point was A and your ending point was also A. However, the direction of travel from A to B is the complete opposite of B to A and therefore they actually cancel each other out when we think in terms of displacement. Going back to the example above, the total return distance between A & B is 1000 meters. The definition of velocity is the rate of change in displacement.ĭisplacement is also a vector quantity which is defined as distance traveled in a particular direction. The concept of velocity is basically speed with a direction.
Velocity – Speed is a scalar quantity (magnitude only) whereas velocity is a vector quantity (magnitude and direction) Sometimes light gates – which emit infrared radiation and are connected to electronic timers – are used to measure accurate timings. You walked a total of 1000m in 2000 seconds and therefore your speed was 1000/2000= 0.50m/s. Imagine you walked from point A to B which is 500 m away, and then returned back to A, and it took you 2000 seconds. Speed – The speed of an object is defined as the change in distance per unit time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
